TALEN-based engineering at PolyGene.
PolyGene offers services based on Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nuclease (TALEN) technology for the speedy generation of constitutive knockout mice, as well as rats and rabbits.
TALEs (Transcription Activator-Like Effectors) are proteins that bind to DNA in a sequence-specific way (Sun and Zhao, 2013). The TALEs are constructed from modularly organized DNA-binding domains, tested and validated in vitro. By fusing such a TALE to a Nuclease (a “TALEN”), a highly specific DNA scissor is made.
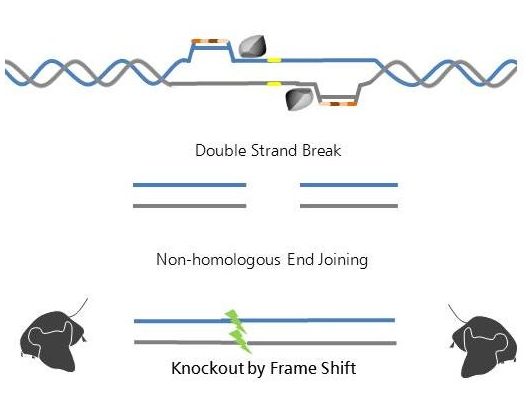
A TALEN acts as a heterodimer (two units of a TALE DNA binding domain (brown, orange) fused to a catalytic domain (grey)), cleaving two close sequences, and thereby increasing specificity to a complexity of 30 – 40 base pairs. Within the cells, TALEN generate double strand breaks which are repaired by Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ). NHEJ is, a natural but error prone repair mechanism that can be used to introduce nucleotide deletions or insertions. This can lead to inactivation or knockout of a target gene.
Within the cells, TALEN generate double strand breaks which are repaired by Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ). NHEJ is, a natural but error prone repair mechanism that can be used to introduce nucleotide deletions or insertions. This can lead to inactivation or knockout of a target gene.
For the generation of other TALE fusion proteins, such as sequence specific activators or silencers, please inquire. TALENs Service Details White Paper on TALENs GET A QUOTE



